Enteric Nervous System Disorders
Enteric nervous system disorders. Inflammatory neuropathy of the enteric nervous system is emerging as an important topic in the field of neurogastroenterology. 10 2021 New research explains how the nervous system in the gut known as the enteric nervous system ENS causes propulsion along the gut highlighting how similar it behaves to other. The enteric nervous system or intrinsic nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract.
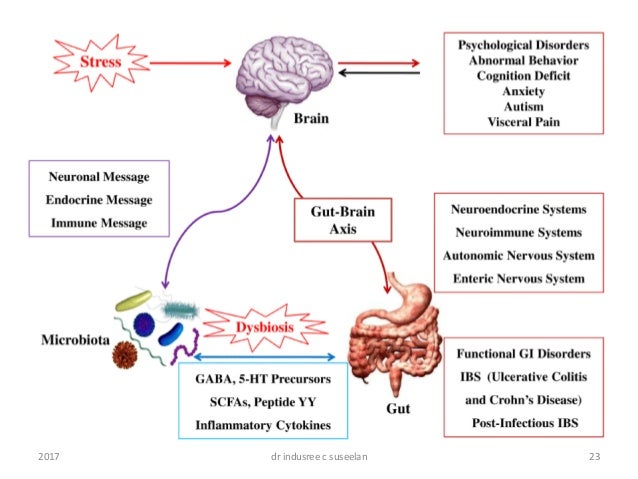
The enteric nervous system doesnt seem capable of thought as we know it but it communicates back and forth with our big brainwith profound results The ENS may trigger big emotional shifts experienced by people coping with irritable bowel syndrome IBS and functional bowel problems such as constipation diarrhea bloating pain and stomach upset. Neuronal cause of death. At the same time the enteric nervous systems response is to slow down or stop digestion.
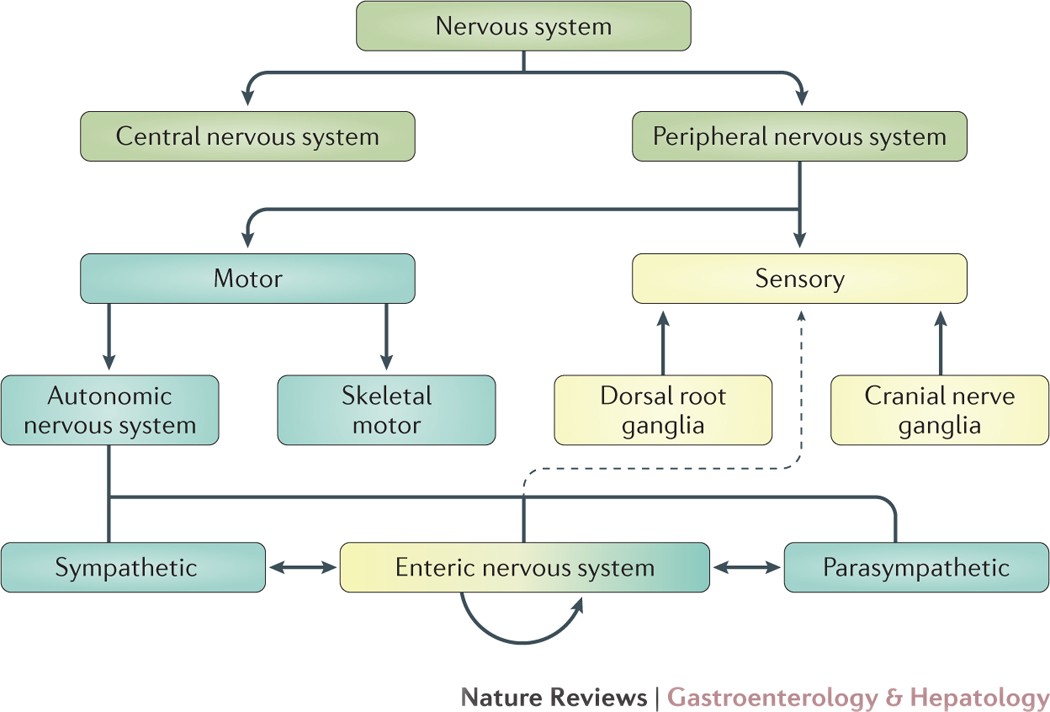
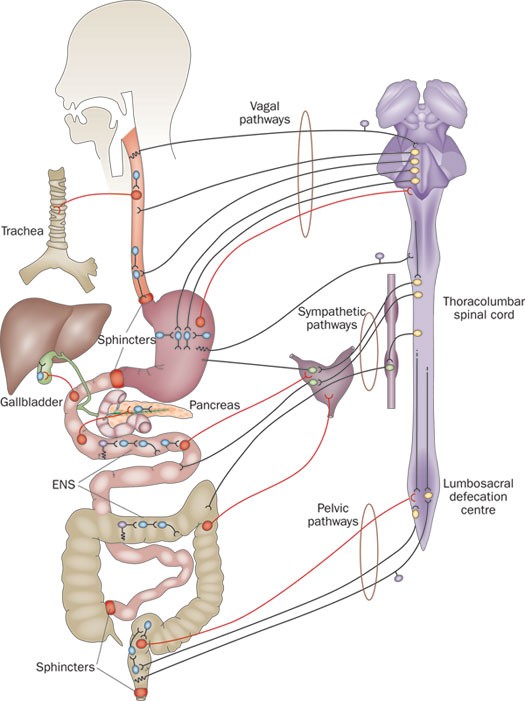
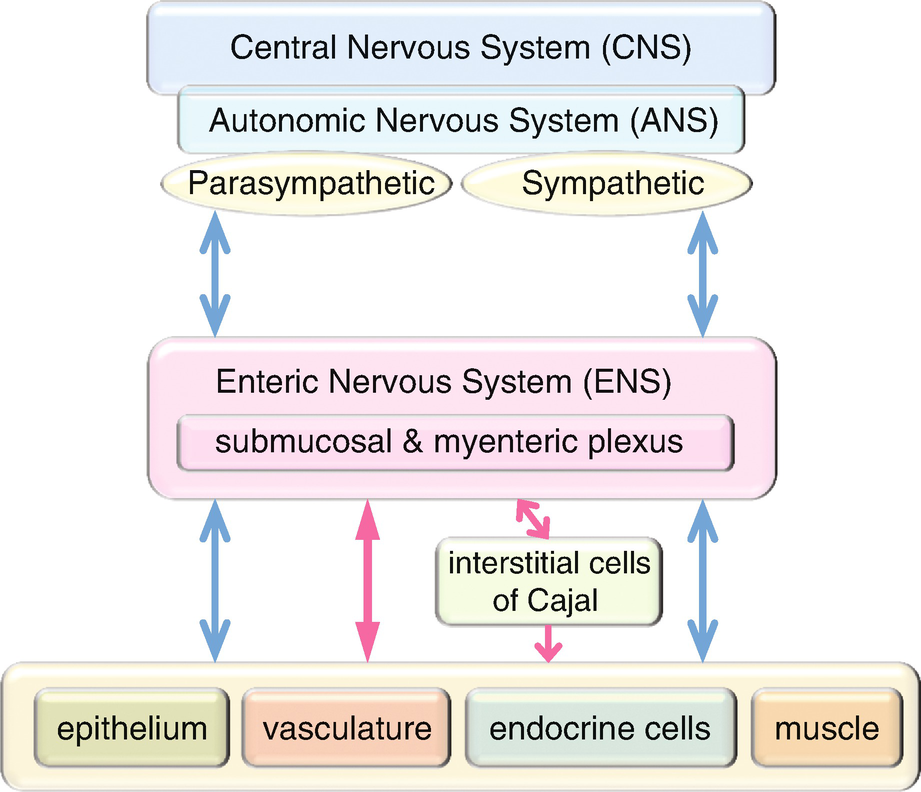
Given the importance size and complexity of the ENS it is not surprising that it. Disorders of the enteric nervous system ENS are manifested as dysmotility and altered secretory function which in turn lead to symptoms of dysphagia diarrhea or. It is capable of acting independently of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems although it may be influenced by them.
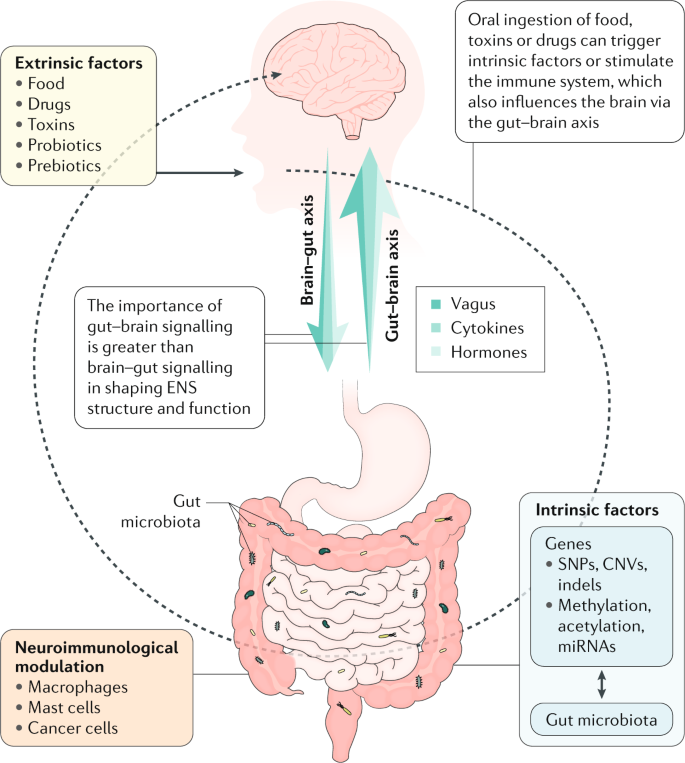
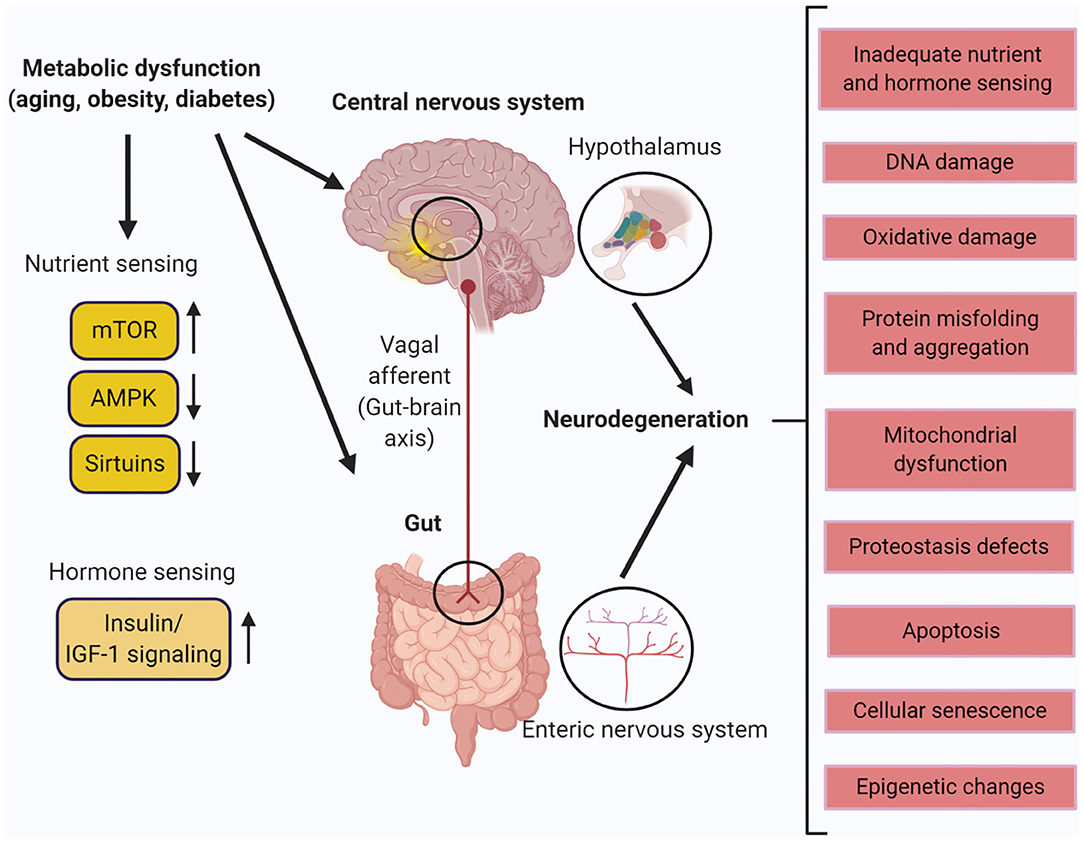
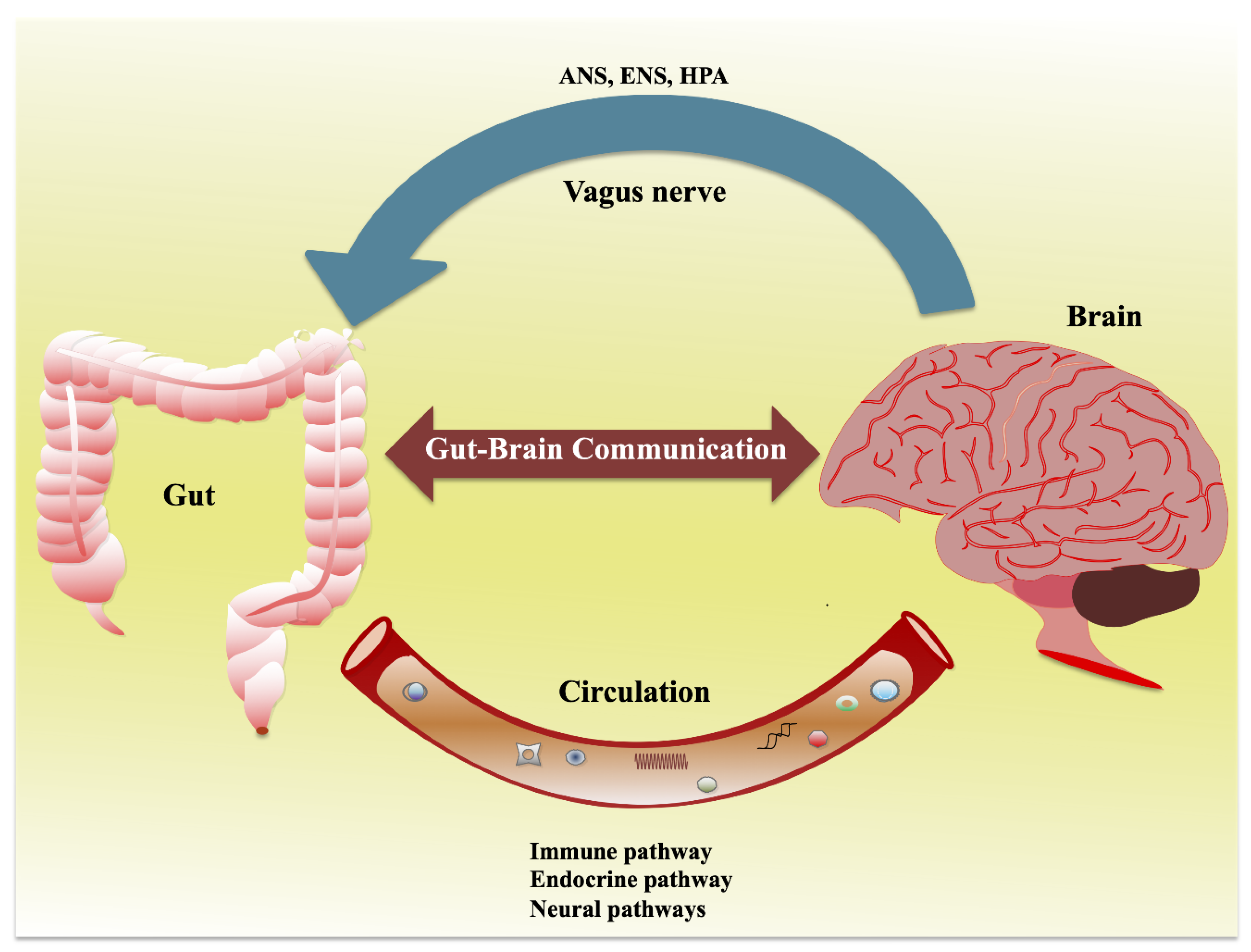
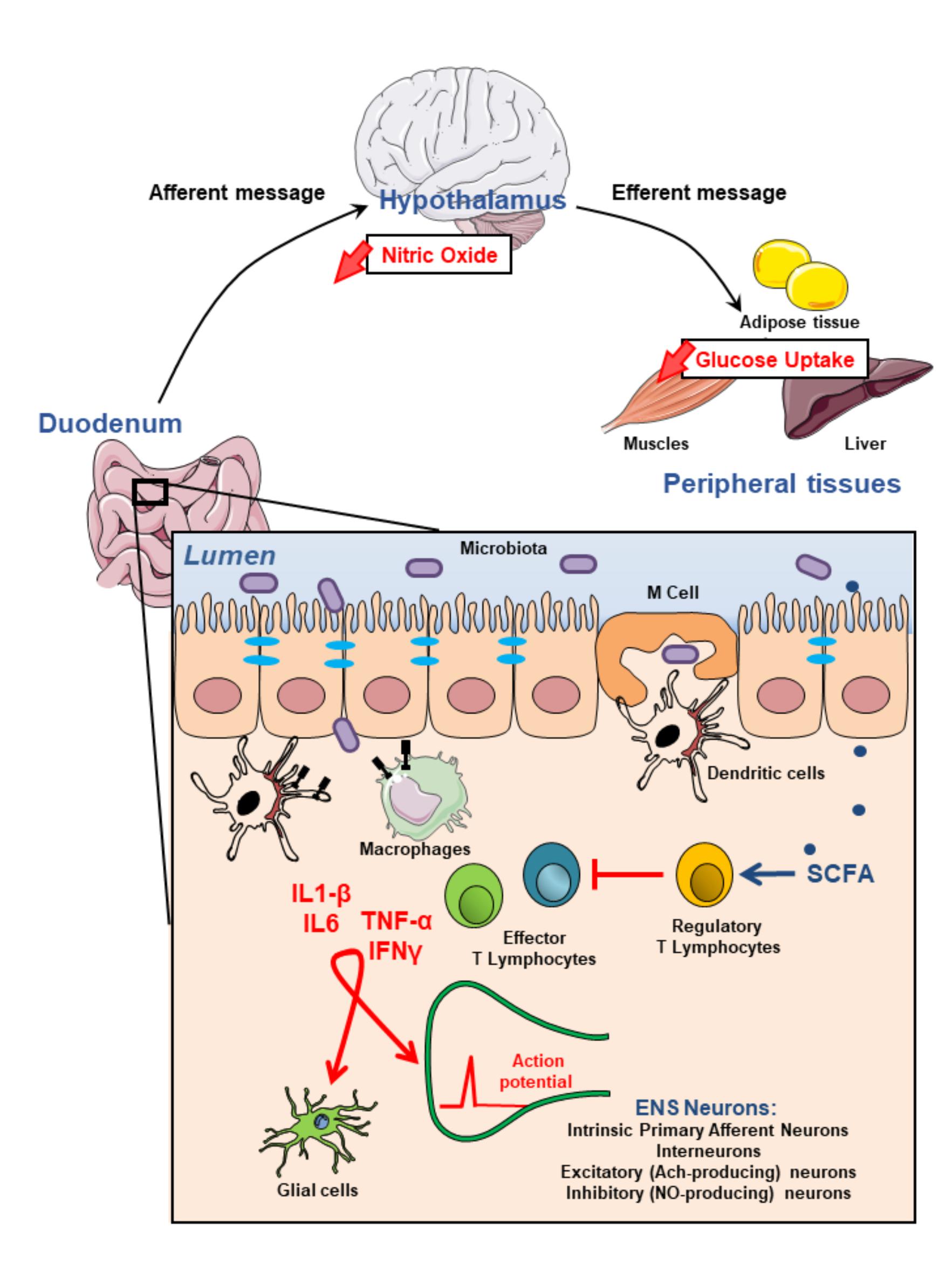
The enteric nervous system ENS is susceptible to various genetic metabolic and environmental threats resulting in clinical disorders characterized by loss or malfunction of neuronal components. In diabetic patients and mice modification of enteric neurons activity in the proximal part of the intestine generates a duodenal hyper-contractility that generates an aberrant message from the gut to the brain. The enteric nervous system ENS is the largest division of the peripheral nervous system and closely resembles components and functions of the central nervous system.
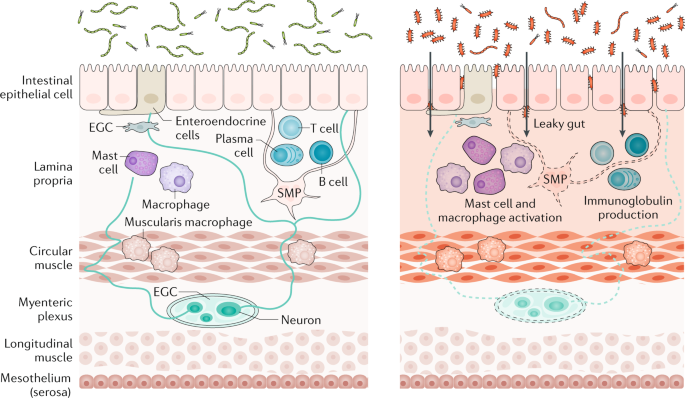
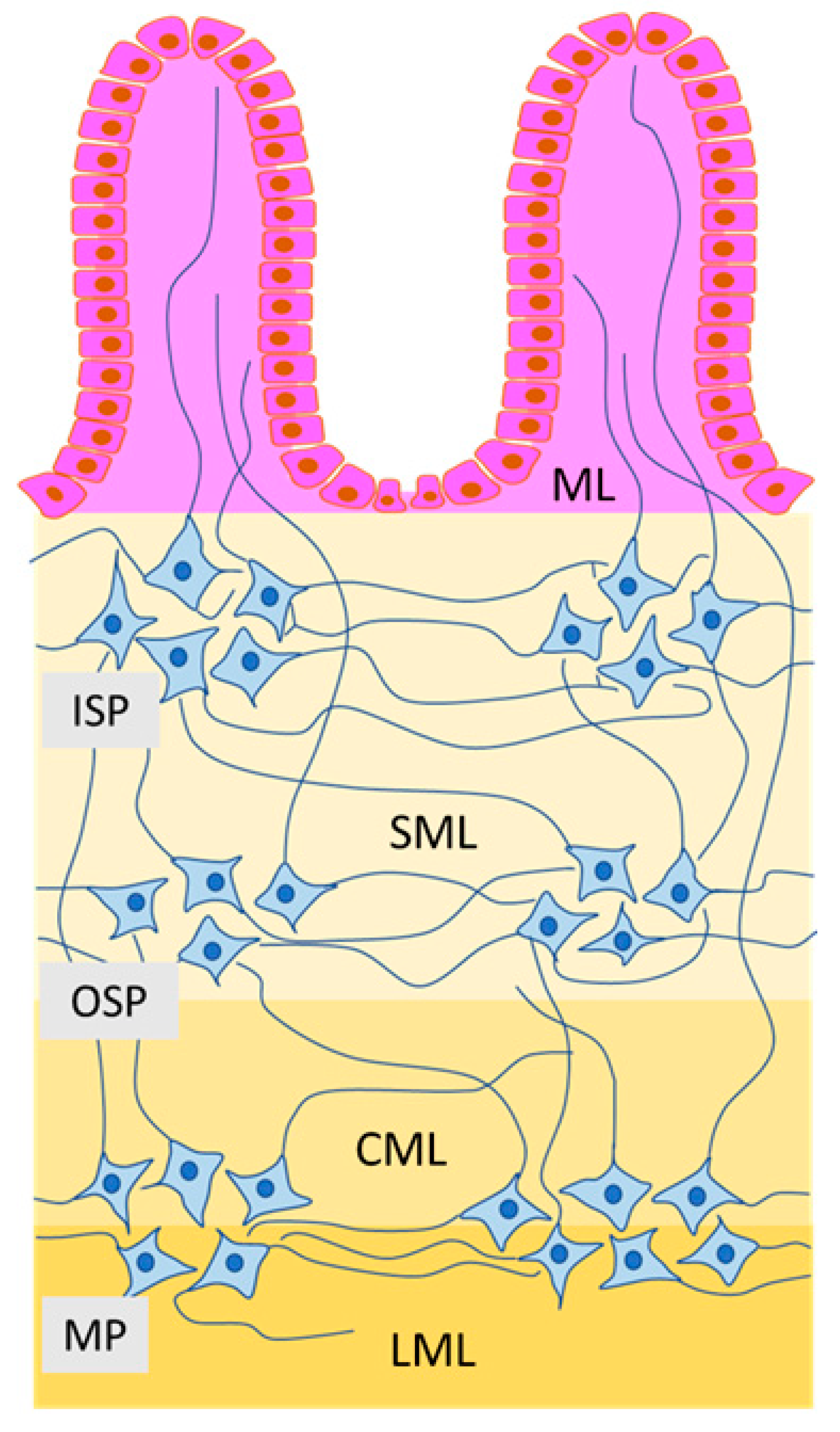
The enteric nervous system is a large collection of neurons located in the walls of the digestive tract along the alimentary canal spanning from the esophagus to the anus. Enteric Nervous System Disorders. At homeostasis enteric nervous system ENS components enteric neurons and enteric glial cells are exposed to and work in concert with the outer and inner microenvironment of the gut to regulate bowel motility transmucosal movement of fluids.
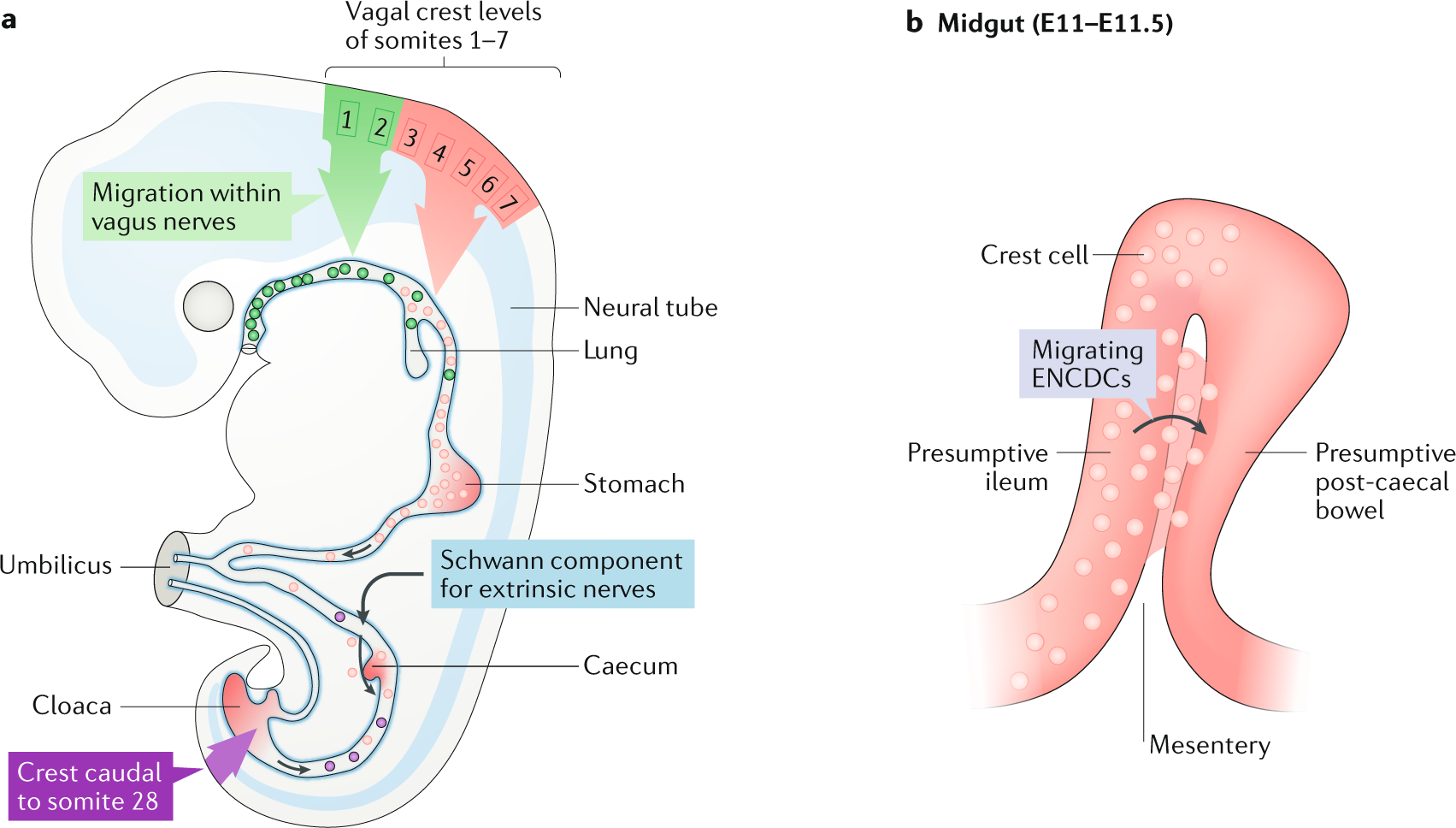
Known as the bodys second brain the enteric nervous system is houses the largest depot of neurons and glia outside of. Primary developmental disorders of the human enteric nervous system can be grouped into those characterised by an abnormal number of neurones hyperganglionosis hypoganglionosis aganglionosis versus abnormal differentiation of neurones biochemical andor physiological1 In each case the clinical presentation may be similar with a. Neurological disorders cause gastrointestinal GI symptoms that are debilitating and markedly diminish quality of life in patients.
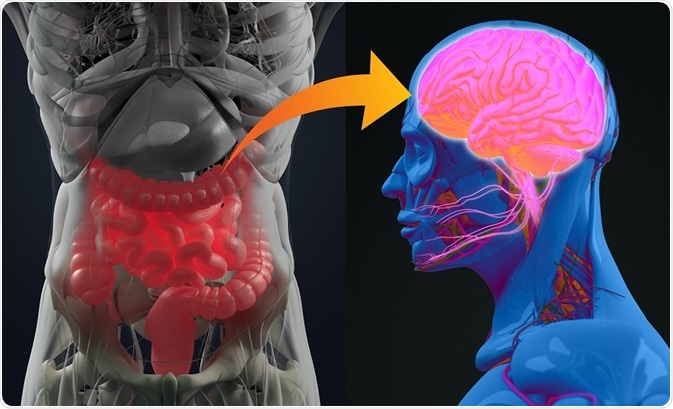
The enteric nervous system as a second brain Life-sustaining functions such as breathing heartbeat blood pressure and body temperature are regulated through the autonomic nervous system. The ENS contains as many neurons as the spinal cord approximately 80-100 million neurons and controls intestinal motility and secretion largely independently of influences from the CNS15 The ENS is affected by Lewy body pathology at early stages of PD67 and by many genetic89 or immune910 neurologic disorders associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility.
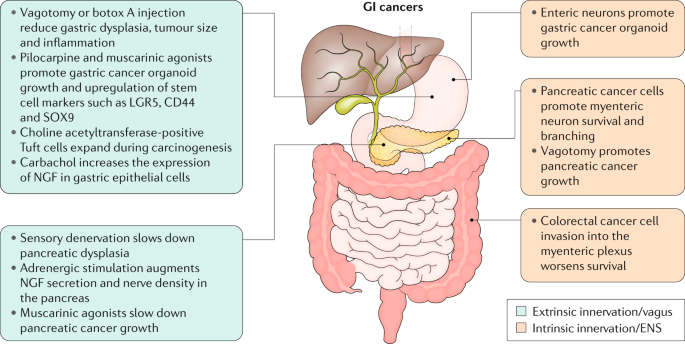
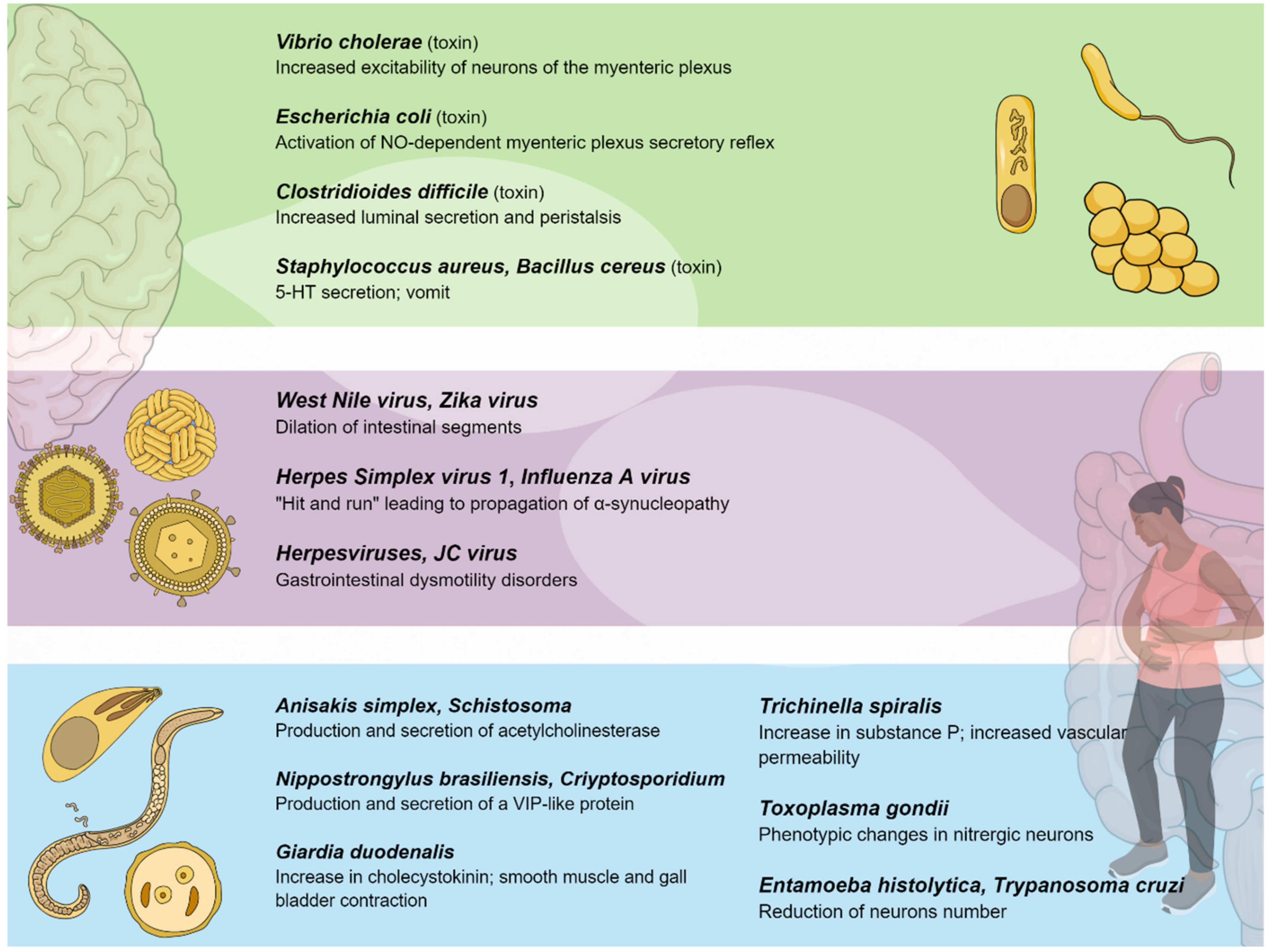
Enteric ganglionitis can be either primary or secondary to a wide array of diseases ie paraneoplastic infectious and neurological disorders and is characterized by a dense infiltrate of inflammatoryimmune cells mainly confined to the neural.
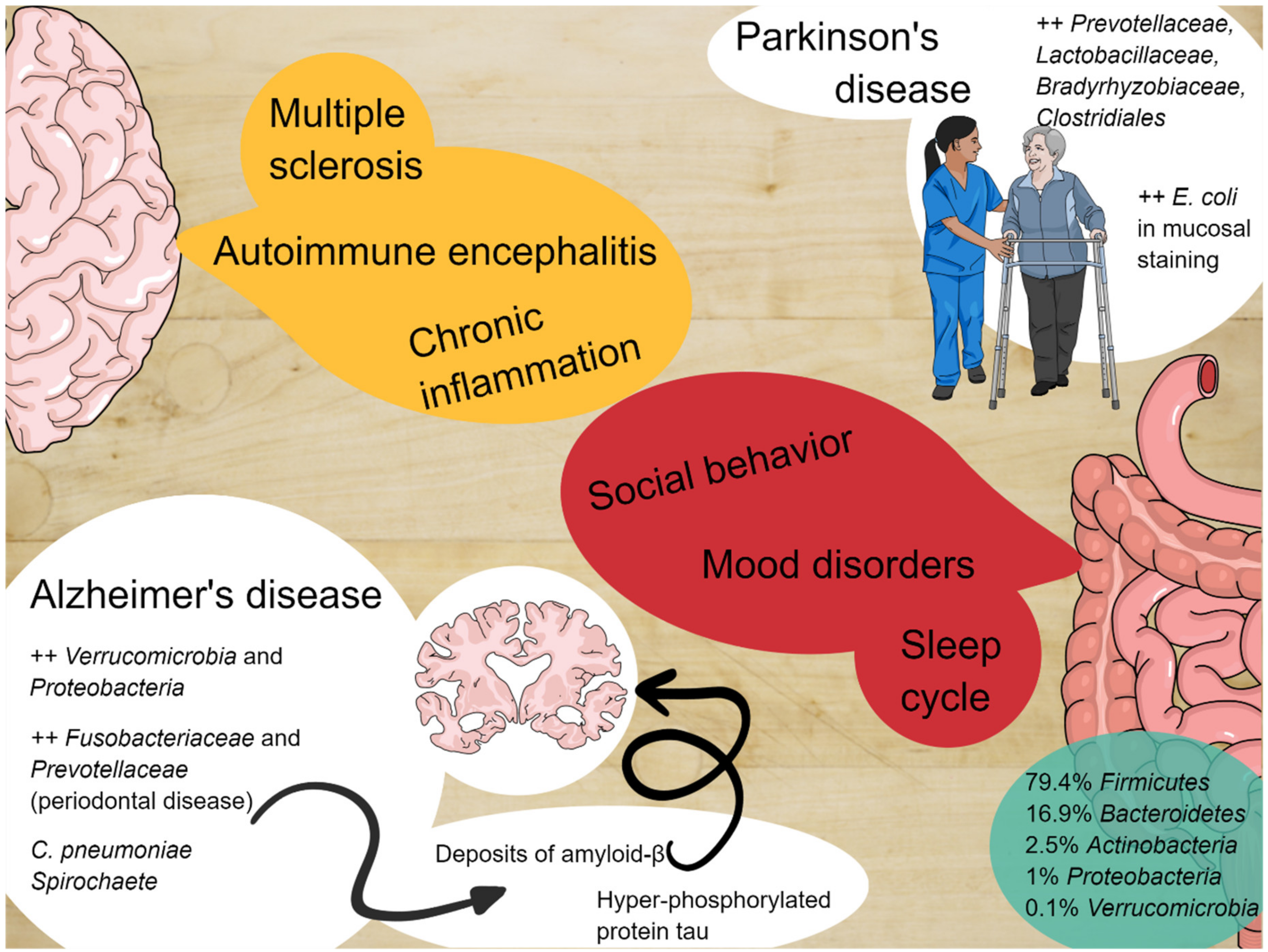
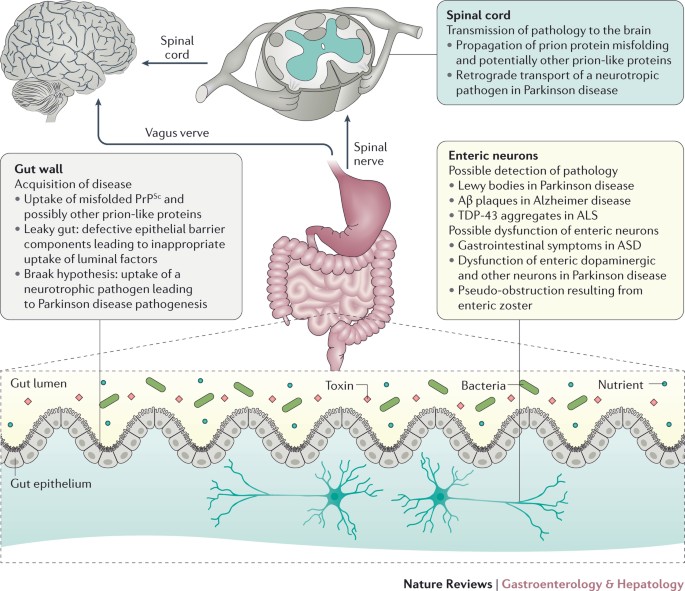
Studies of autism and neurodegenerative disorders have shown that the. Unsuspected viral infection of the ENS. The enteric nervous system as a second brain Life-sustaining functions such as breathing heartbeat blood pressure and body temperature are regulated through the autonomic nervous system. Graphical representation of gastrointestinal disorders from an enteric nervous system perspective. 10 2021 New research explains how the nervous system in the gut known as the enteric nervous system ENS causes propulsion along the gut highlighting how similar it behaves to other. At the same time the enteric nervous systems response is to slow down or stop digestion. The enteric neuromusculature may also become involved in a variety of connective tissues disorders including systemic sclerosis systemic lupus erythematosus and dermatomyositis. The ENS is also. The enteric nervous system doesnt seem capable of thought as we know it but it communicates back and forth with our big brainwith profound results The ENS may trigger big emotional shifts experienced by people coping with irritable bowel syndrome IBS and functional bowel problems such as constipation diarrhea bloating pain and stomach upset.
Given the importance size and complexity of the ENS it is not surprising that it. The bowel and beyond. Studies of autism and neurodegenerative disorders have shown that the. The enteric neuromusculature can be affected by a wide variety of other conditions or affected by toxic agents drugs and irradiation. The enteric nervous system ENS is susceptible to various genetic metabolic and environmental threats resulting in clinical disorders characterized by loss or malfunction of neuronal components. Disorders of the enteric nervous system ENS are manifested as dysmotility and altered secretory function which in turn lead to symptoms of dysphagia diarrhea or. This is done so that more of the bodys energy can be diverted to the situation causing the threat.






























Post a Comment for "Enteric Nervous System Disorders"